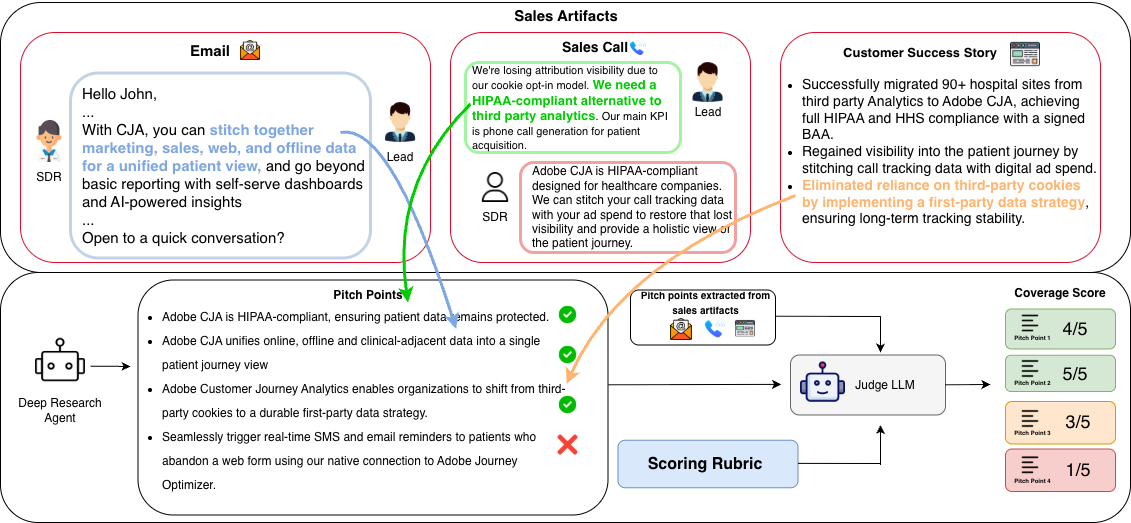
- STORM-QWEN-2.5 achieves the highest aggregate scores on SDR-Bench.
- Deep research agents excel in Healthcare; a "personalization plateau" exists in
Tech when compared against e-mails as ground truth.
- GEMINI-2.5-PRO-DR scores highest on the subset but risks data leakage.
- Deep research agents offer superior resolution but at significantly higher inference costs.
The experimental results across various ground truth artifacts reveal distinct performance patterns
between standard LLMs and deep research agents. STORM-QWEN-2.5 emerged as the most robust
performer for the SDR-Bench testbed, achieving an aggregate Weighted Coverage Score (WCS) of
42.51 for success stories and 30.43 for sales transcripts (proprietary data). This
suggests that multi-turn, search-augmented research workflows are particularly effective at synthesizing
the strategic alignment necessary to reconstruct the logic of complex, real-world deal closures. We
observe the trend remains consistent across different industries, suggesting that multi-turn research
workflows are uniquely capable of reconstructing the complex logic of real-world deal closures. Notably,
for a public dataset, we find a narrow performance margin between GPT-4o with web-search
(39.77) and STORM (41.59). Despite this small delta in strategic coverage,
GPT-4o required a significantly lower token budget. For enterprise scale deployments, where latency and
cost are critical—leveraging high-performing LLMs with direct tool-calling represents a more
computationally efficient frontier than the marginal gains offered by high-overhead research
agents.
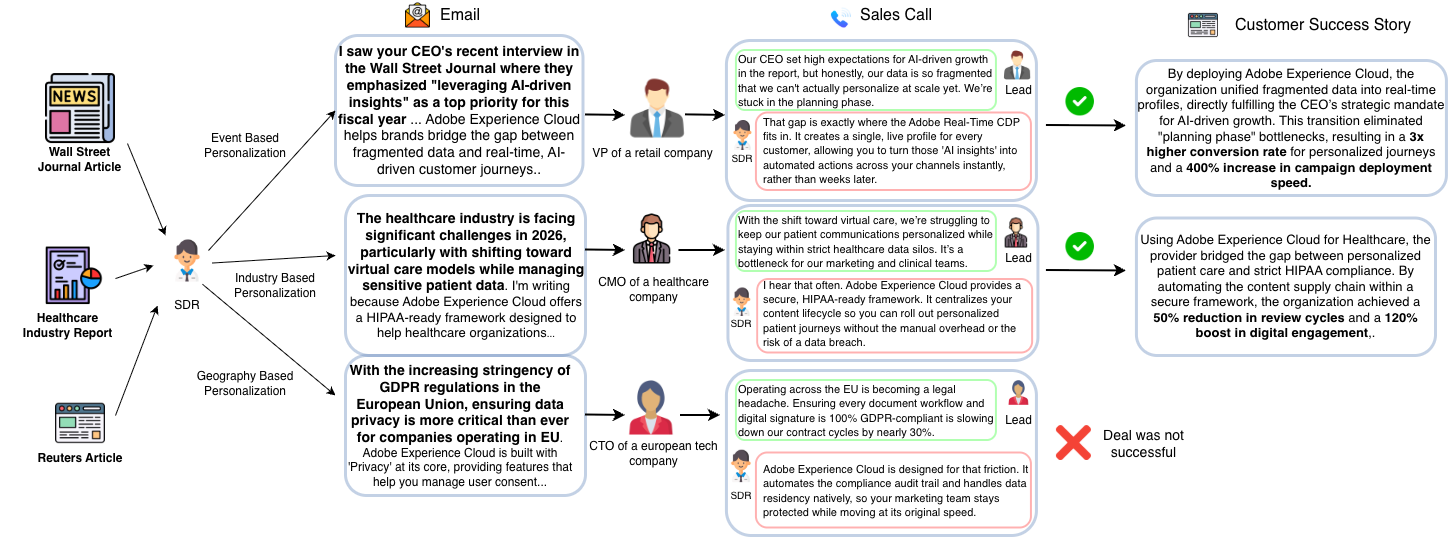
When analyzing the Enterprise Sales Email dataset (SDR-Leaderboard), a
notable divergence appears between industry sectors. In the Healthcare cohort, deep research
agents
like STORM and ODR demonstrated a significant performance delta, scoring notably higher
on successful outreach emails (e.g., STORM at 32.27) compared to unsuccessful outreach emails
(22.46). This indicates that these agents are proficient at capturing the specific
personalization cues that drive engagement in specialized, high-stakes sectors.
Conversely, in the Tech cohort, performance scores remained relatively uniform across all models
and outcomes. This exhibit a "personalization plateau", showing no statistically significant performance
difference between successful and unsuccessful outreach sets. This suggests that while models generate
coherent content, there remains a critical gap in their ability to produce the strategic depth required to
drive real-world revenue in highly competitive markets.
While GEMINI-2.5-PRO-DR achieved the highest score on the 25-story subset (62.63), it is
critical to note that this model was evaluated outside the strict enforcement of the
SDR-Playground's historical internet constraints. Consequently, the risk of "future data
leakage", where the model accesses post-hoc analyses or the success story itself, is substantially
higher. This underscores the necessity of our time-restricted simulation (Wt) for valid
benchmarking.
Finally, while deep research agents provide superior strategic resolution, they involve a significant
computational trade-off. The iterative nature of STORM and ODR requires substantially higher
inference costs compared to standard LLM-plus-web-search configurations, presenting a clear bottleneck for
personalization at enterprise scale.